
Если и есть одно слово, которое может заставить сердце родителя сжаться, так это «рак». К сожалению, наши питомцы не избавлены от этой страшной болезни, как бы нам этого ни хотелось. Как и у людей, у домашних животных может развиться множество видов рака, одним из которых является плоскоклеточный рак (SCC). Продолжайте читать, чтобы узнать больше о плоскоклеточном раке у домашних животных и о том, как его предотвратить.
Плоскоклеточные клетки представляют собой тонкие, плоские клетки неправильной формы, составляющие эпителий, выстилающий наружный слой кожи и внутренних органов. Эти клетки выполняют множество функций, одна из которых — защита подлежащих тканей. Когда плоскоклеточные клетки повреждаются по таким причинам, как воздействие ультрафиолетового излучения или табачного дыма, они могут стать раковыми.
Хотя плоскоклеточный рак может развиться как у собак, так и у кошек, этот рак гораздо чаще встречается у кошек, чем у собак, особенно у кошек среднего и старшего возраста. Существует два основных типа плоскоклеточного рака у домашних животных:оральный и кожный.
По данным DVM360, это местно-агрессивный рак. Плоскоклеточная карцинома полости рта составляет 10% всех случаев рака полости рта у кошек и является вторым наиболее распространенным раком полости рта у собак. Он обычно поражает пожилых животных и имеет низкую выживаемость. Хотя его можно найти в любом месте рта, например, на миндалинах и деснах, оральный плоскоклеточный рак чаще всего появляется под языком. Он быстро растет и часто поражает челюстную кость.
У кошек канцерогены, такие как сигаретный дым и химические вещества против блох, которые попадают на язык кошки во время ухода за ней, могут вызвать оральный SCC. Точная причина у собак пока неизвестна.
Признаки плоскоклеточного рака полости рта включают неприятный запах изо рта, трудности с приемом пищи, слюнотечение, а также кровотечение из полости рта и боль. Другие симптомы включают шатание зубов и изъязвление десен. These signs can often be confused with dental disease, so it is essential for veterinarians to perform a thorough oral exam in older pets. Diagnostic procedures are the same for oral as for skin cancer, which can start with labwork, needle aspirate and/or biopsy with histopathology.
Surgery is the standard of treatment for oral SCC. It can be aggressive, with the removal of a portion of the jawbone, nearby lymph nodes, or both, if necessary. Although surgical tumor removal can provide immense pain relief, the tumor’s size and location can sometimes make surgery difficult or even impractical. Non-surgical treatment options include chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Treatments that do not target the tumor itself, but can help a pet to feel better, include antibiotics, painkillers, and nutritional supplementation.
Prevention strategies include the following:

“My 8-year-old dachshund-Jack Russell mix was diagnosed with squamous cell cancer of the tonsils,” begins pet parent Elizabeth. “When I brought her to the vet, she had lost weight, had no bark, and seemed to have difficulty eating. The vet found and removed the tumor, but warned me that this is an extremely aggressive form of cancer and that it had most likely already metastasized to her lymph nodes.” Elizabeth was referred to an oncologist, who discovered more lesions in Lola’s lung. They recommended palliative radiation and sadly, gave Lola only 3 months to live.
“I could not just let her die,” says Elizabeth. “So I read all the veterinary and animal literature I could find on what deters cancer cells in animals. The finding that stood out to me was cruciferous vegetables, like broccoli, kale, and Brussel sprouts, have been found to inhibit cancer cells in research on animals.” Elizabeth dived deeper and changed her dog’s diet:“She is a very picky eater, but likes Brussel sprouts, as long as they have butter in them. Also a diet low in carbs, high in protein and with healthy fats was found to be helpful! She has been eating Brussel sprouts with olive oil and a little butter every day, as well as chicken breast. I’d like to get some other fruits and veggies into her, but she won’t eat them.”
While vets and pet parents alike will tell you that cancer is a daunting diagnosis and that it is truly hit-or-miss with alternative solutions, Elizabeth has had success with Lola’s diet. “It is now 3 months post diagnosis. She has regained her weight and her bark, and to all appearances is symptom free, active, and happy. It’s too early to know if she will be a survivor, but I am sharing this in case anyone else’s dog is in a similar position. So far, she is defying the odds. By the way, she may be the cutest and most wonderful dog on this earth— an unbiased opinion.” Lola’s claims have totaled $2,919 and Elizabeth has been reimbursed $2,135 (90% reimbursement rate; $250 deductible). Please note that cancer claims were sandwiched between unrelated claims that may skew the totals.
Skin SCC is the fourth most common feline skin cancer but is rare in dogs. Excessive sun exposure is the most common cause. By far, white and light-colored hair cats are most susceptible to skin SCC and often develop tumor lesions on the temples, eyelids, tip of the nose, and outer tips of the ears. Dogs with sparse hair and lightly pigmented skin and fur (e.g., white Bull Terriers) are also susceptible. Interestingly, in some dogs, skin SCC can target the nailbeds.
Skin SCC typically affects older cats, but both dogs and cats of any breed and age can develop this cancer, depending on their amount of sun exposure and lack of skin pigmentation.
In the early stages, skin SCC doesn’t even look like a tumor. Instead, you might notice a small, solitary skin lesion that looks a little dry, flaky, and ulcerated. Often, these signs can be mistaken for other skin diseases, such as allergies or parasites. As time goes on, the lesion grows, becomes bumpy, develops hard and irregular borders, and causes skin swelling.
Skin SCC rarely spreads beyond its original tumor site, but it can spread to nearby lymph nodes and possibly the lungs. It can also recur in the same spot.
Diagnosing skin SCC is done via a skin biopsy, which will show cancerous squamous cells. Other diagnostic tools include a blood sample, chest x-ray, and lymph node analysis to devise an optimal treatment plan.
Skin SCC is primarily treated with aggressive surgical removal of the lesion and at least a portion of the affected area to ensure removal of all tumor tissue. Other treatments include radiation therapy, cryotherapy (freezing), and chemotherapy.
Squamous cell carcinoma is an aggressive cancer in pets. Pay close attention to your pet’s skin, particularly if you have a white-haired cat, and take your pet to your veterinarian if you notice any strange bumps on the skin or oral problems. The optimal treatment plan will depend on the tumor’s size and disease progression.
If you love your pets like family, you want to protect them like family. By enrolling in pet insurance, you can save up to 90% on vet bills which means saying “yes” to life-saving treatments, no matter the cost. If you’re not a part of our pack, start by getting a free quote.
The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional veterinarian advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your veterinarian or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical diagnosis, condition, or treatment options.

В тот или иной момент каждый любитель собак сталкивался с неприятным запахом изо рта от своего пылкого собачьего компаньона. Зловонное дыхание настолько распространено среди собак, что сама фраза стала оскорблением, например:«Отойди, собачье дыхание!» Тем не менее, упоминание об идее профилактическ
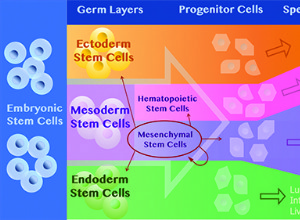
В то время в прошлом году я не знал, что терапия стволовыми клетками для животных существует. В поисках работы, где я мог бы использовать свои знания в области биологии и любовь к животным, я нашел вакансию специалиста по стволовым клеткам в местном ветеринарном кабинете. Я получил работу! – и обнар